Problem Statement:
With increasing security and safety concerns, AEM Groovy Console is not allowed to be installed in the author/publish environment in Production. As a result, users require an alternative tool to execute short scripts for content updates.
Requirement:
The Groovy Console has been a preferred tool for executing short scripts for content updates in Adobe Experience Manager (AEM), but due to security and safety concerns, the console is not installed in the author/publish environment in Production. This article explores using the ACS Commons Managed Control Process (MCP) as a better alternative for running bulk updates with the provided console. It provides an introduction to MCP and explains how to extend it in a current project structure and make relevant POM changes. It also covers tools that come out of the box with MCP, how to use and maintain them, and how to create a new process and form fields with MCP.
Extend MCP in your current project structure and add the relevant POM changes
Introduction:
MCP (Manage Controlled Processes) is both a dashboard for performing complex tasks and also a rich API for defining these tasks as process definitions. In addition to kicking off new processes, users can also monitor running tasks, retrieve information about completed tasks, halt work, and so on.
The Groovy console is an awesome tool to write short scripts to execute some of the content updates but due to increase security and safety issues, the AMS team is not allowing to install Groovy Console in the author/publish environment in Production and there is no other way we can run the groovy console on pubs. Hence ACS Commons MCP would be the better replacement for running these kinds of bulk updates using the beautiful console provided by ACS Commons.
How to use MCP?
Process Manager: How to navigate and access ACS Commons MCP process manager
Tools: Tools that come to OOTB when you use MCP tools
Operations: How to use and maintain the MCP process
In order to extend the MCP process, create a separate module called MCP under your project directory and add the following dependencies as shown below:
Add the following code into all module pom.xml to embed this new module
<dependency>
<groupId>com.adobe.acs</groupId>
<artifactId>acs-aem-commons-bundle</artifactId>
<version>5.0.4</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>Create the packages and start your first process:
For the MCP process to pick up your new process, you need to create a service that implements ProcessDefinitionFactory and override the getName method to provide the process name to show under the list of processes.
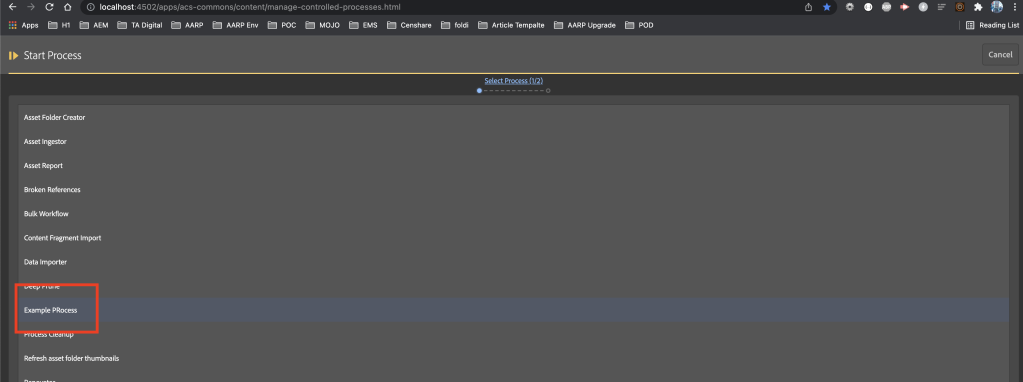
createProcessDefinitionInstance to create a new instance of this process.
package com.mysite.mcp.process;
import org.osgi.service.component.annotations.Component;
import com.adobe.acs.commons.mcp.ProcessDefinitionFactory;
@Component(service = ProcessDefinitionFactory.class, immediate = true)
public class ExampleProcessFactory extends ProcessDefinitionFactory<ExampleProcess> {
@Override
public String getName() {
return "Example PRocess";
}
@Override
protected ExampleProcess createProcessDefinitionInstance() {
return new ExampleProcess();
}
}
You can learn more regarding process definition here
Create Process Implementation:
The process implementation class extends ProcessDefinition and you can have multiple form fields to accept the author’s input.

You can learn more about form fields here
You need to override:
init – to run initialize the process
build process – define the Action and add the description of the process
store report – Basically used to save the action results under the specified path
package com.mysite.mcp.process;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.EnumMap;
import java.util.List;
import javax.jcr.RepositoryException;
import org.apache.sling.api.resource.LoginException;
import org.apache.sling.api.resource.PersistenceException;
import org.apache.sling.api.resource.ResourceResolver;
import com.adobe.acs.commons.fam.ActionManager;
import com.adobe.acs.commons.mcp.ProcessDefinition;
import com.adobe.acs.commons.mcp.ProcessInstance;
import com.adobe.acs.commons.mcp.form.FormField;
import com.adobe.acs.commons.mcp.model.GenericReport;
public class ExampleProcess extends ProcessDefinition {
private static final String REPORT_SAVE_PATH = "/jcr:content/report";
private final List<EnumMap<ReportColumns, Object>> reportRows = new ArrayList<>();
GenericReport genericReport = new GenericReport();
@FormField(name = "Enter Text",
description = "Example text to be reported",
required = false,
options = {"default=enter test text"})
private String emapleText;
@Override
public void buildProcess(ProcessInstance instance, ResourceResolver rr) throws RepositoryException, LoginException {
genericReport.setName("exampleReport");
instance.defineCriticalAction("Running Example", rr, this::reportExampleAction);
instance.getInfo().setDescription("Executing Example Process");
}
protected void reportExampleAction(ActionManager manager) {
record(emapleText);
}
private void record(String emapleText) {
final EnumMap<ReportColumns, Object> row = new EnumMap<>(ReportColumns.class);
row.put(ReportColumns.SERIAL, 1);
row.put(ReportColumns.TEXT, emapleText);
reportRows.add(row);
}
@Override
public void storeReport(ProcessInstance instance, ResourceResolver rr) throws RepositoryException, PersistenceException {
genericReport.setRows(reportRows, ReportColumns.class);
genericReport.persist(rr, instance.getPath() + REPORT_SAVE_PATH);
}
@Override
public void init() throws RepositoryException {
}
public enum ReportColumns {
SERIAL, TEXT
}
}
you can learn more about the process lifecycle here
Once the execution is complete we can save and see the report results:


References:
https://adobe-consulting-services.github.io/acs-aem-commons/features/mcp/index.html
